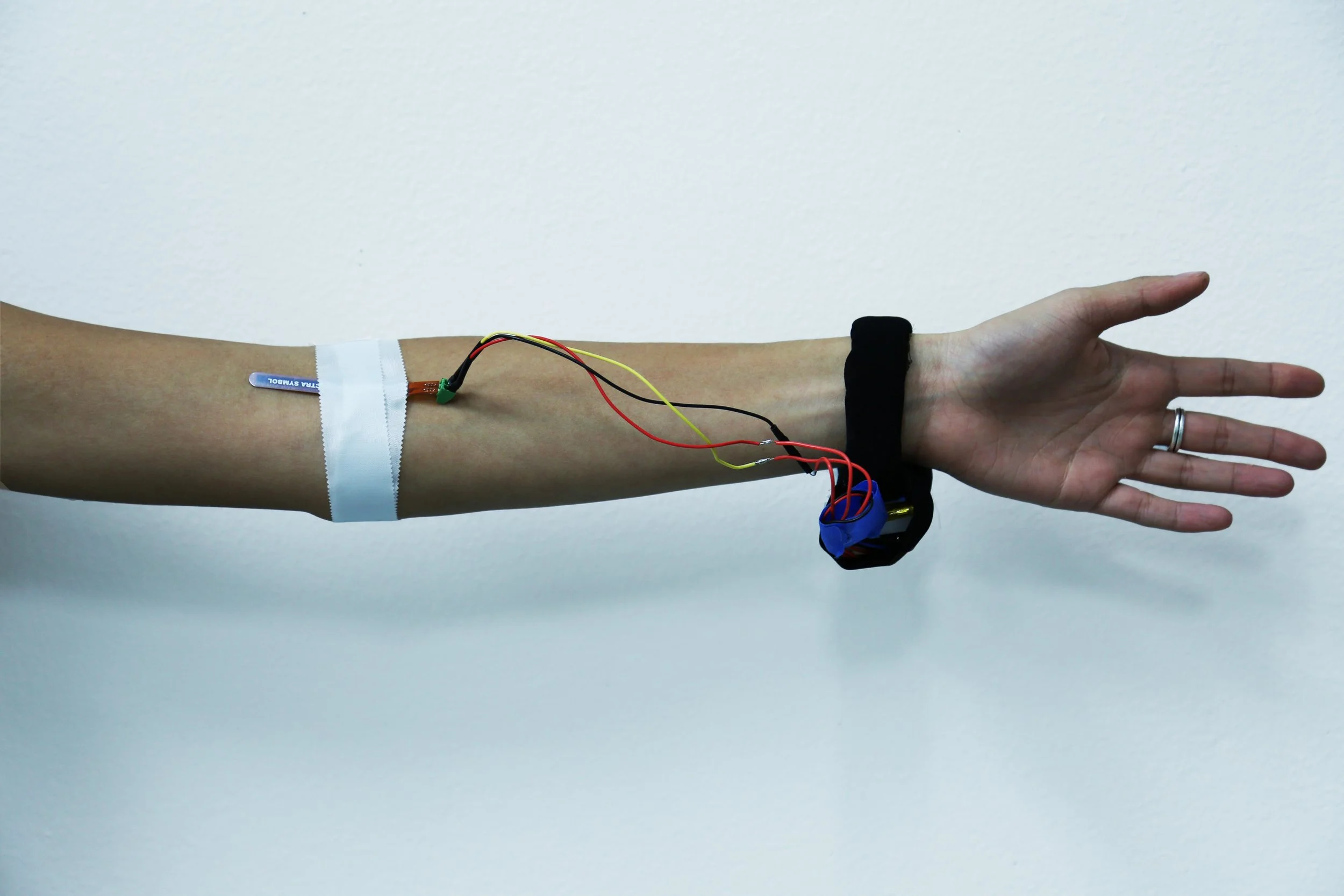
Notes: Internal Sound Diary
A person with Alzheimer’s goes through stages of memory loss. I wanted to create an internal wearable that reflects a person’s cognitive emotions and gestures to trigger their memories and familiar patterns. This wearable will benefit the person when they are in the early/ moderate stages of Alzheimer’s until their helpless in the later stage when they need full assistance from a family member or caretaker.
I didn’t want to find a cure for Alzheimer’s, but a device that will help slow down memory loss for the person. The person might feel helpless at times, where they might not feel in control. The device will allow them to gain confidence by triggering their internal memories where they are able to be back in control, by not being controlled or relied on a device or someone else.
Since scientists are looking for a cure for Alzheimer’s and Dementia. I have researched techniques that scientists/ caretakers have used to help with memory loss. Using vibrations and rhythmic sounds help stimulate memories that are hidden in parts of the brain.
Categories UX Design, Design Research, Prototyping
Topics Wearable Product, Embodiment, Human-Computer Interaction
Tools Processing, Arduino, Adobe Suite
EFFECTS OF PEOPLE WITH ALZHEIMER’S
- Fear of losing who they are
- Being in control and not in control
- Can see the words, but can’t reach them
- Naming, Planning sequence, calculations
- Loss of Memory - Loss of relationships
- Change in personality/behavior
- Takes away their confidence
- Helpless
- Relies on other people
PEOPLE EFFECTED BY AN ALZHEIMER’S PATIENT
- Staging/ Slow Goodbye
- The patient might not understand their losses
- Steals the patient from their close ones
- They become a different person. Have to remember that isn’t them
SCENARIO 1: NAVIGATING/PATTERN
A person navigating through a familiar space, such as their home they tend to follow a pattern or routine. As they begin to lose their memory and forget, they become confused or scared. The device will become activated by a tone in their voice or interpret their body language and gestures. A familiar sound or music begins to play to help them follow their own instincts and return to their patterns.
There will be a repertoire of music assigned to each room for no confusion or overlap. As they begin to move through the space they will realize the volume will increase or decrease to indicate the direction to their destination.
Sound:
Louder = They are getting closer to their destination.
Softer = They are getting further away or going the wrong direction.
Once the person gets closer, the sound will transfer to a standing device in the room, communicating they have reached their destination. If they haven't reached their destination after a period of time, an additional alert is activated to become full assistance and instructing them directions. Also informing a family member or caretaker for extra assistance.
Ex: Forgetting where the bathroom was but said the word “bathroom”. Will vibrate and of a pulse rhythm indicating you are going the right way.
Gestures: grabbing the wrist, head moving around in a faster pace (confusion)
SCENARIO 2.: FAMILIARITY/ RELATIONSHIPS (Facial-Sound Recognition)
Voice recordings that will help identify a particular family member or friend. If the person with Alzheimer's placed in a social setting and not able to recognize the other person, the wearable device will activate based on their gestures or by hearing the tone of their voice. The voice recording will be a form of a reminder of a certain memory sound, such as the partner saying their name or a phase. To help activate the memory of their relationship and allow them to continue a smooth communication with the other person.
Ex: Wife/Husband coming home and kisses or tries to kiss the significant other with Alzheimer’s will activate. The gesture is the touch of the face/ voice and the movement of the neck bending or bending the arm will only start of the recording. If the wife or husband in making the gesture there wedding song comes on where it will trigger their memories of the person.
Transferring Gestures: hugging, a kiss, holding hands, touching the shoulder
REFLECTION
It was interesting on how intimate and personal a wearable device can become a person. A person with Alzheimer's or anyone with health issues or none at all, having the choice of what they wear defines a lot of who a person is. The wristband, for instance, is a personal and private activity for the wearer.
Which it can assist a person when they are in need and also giving them control, but keeping their confidence up. It is also interesting how using the wearable band can not just help a person with Alzheimer's, but also maybe a person who might be blind. Using music and sound as a tool for navigating through space and warn them if they are too far or in the right location they need to be. Researching other technology wearables or devices used for navigating, I saw that creating a secret machoism, such as smell, sounds, or pulse devices. These techniques might be a way help notify the person/user allows them to make their own decision based on patterns and familiar situations and not lose control of who they are.
RESEARCH 1: Music: Typically, “stimulative music” activates, while “sedative music” quiets. Stimulative music, with percussive sounds and fairly quick tempos, tends to naturally promote movement, such as toe taps.
RESEARCH 2: Ultrasound: The researchers in Australia used multiple iterations of scanning ultrasound on the mouse’s brain, and the high-frequency sound waves activated the microglial cells, which in turn digested the amyloid beta plaques. The ultrasound causes only a temporary opening past the blood-brain barrier, so its protective role is quickly restored following the clearing of the plaque.